The debate between nature and nurture has long intrigued researchers, philosophers, and psychologists seeking to understand the factors that shape human behavior. While genetics (nature) and environment (nurture) both contribute to shaping who we are, exploring their interplay can provide valuable insights into how individuals develop and behave. This article delves into the complex relationship between genetics and environment in influencing our behaviors.
The Role of Genetics

Genetics refers to the hereditary information passed down from parents to offspring through genes. These genes contain instructions that determine various physical traits as well as aspects of our behavior. Here are some key considerations regarding genetic influence on behavior:
Inherited Traits
Certain behavioral traits have a strong genetic component. For example, intelligence, temperament, personality traits like introversion or extroversion, susceptibility to mental disorders such as depression or schizophrenia – all show evidence of being influenced by genetics.
Genetic Predispositions
Genetic predispositions indicate an increased likelihood for certain behaviors or conditions based on an individual’s genetic makeup. For instance, someone with a family history of alcoholism may have a higher risk of developing alcohol addiction due to inherited genetic factors.
Gene-Environment Interaction

It is essential to recognize that genes do not act in isolation but interact with environmental factors in shaping behavior. Gene-environment interactions occur when specific genes’ effects depend on particular environmental circumstances or experiences.
The Impact of Environment
While genetics lay the foundation for potential behavioral tendencies, it is crucial to acknowledge the powerful role played by environmental influences throughout life:
Early Childhood Experiences

Early childhood experiences significantly impact development and behavior later in life. Factors such as parental upbringing styles, socioeconomic status, education level within the household can shape cognitive abilities, social skills development,and emotional well-being.
Cultural Influences
Culture plays a significant role in determining societal norms, values, and expectations. Cultural influences shape behavior through socialization processes, as individuals learn and adopt specific behaviors from their cultural surroundings.
Social Interactions

Interactions with peers, family members,and the broader social environment greatly impact behavioral outcomes. These interactions can influence everything from communication styles to moral beliefs and attitudes towards certain issues.
The Complexity of Nature vs. Nurture
Understanding human behavior requires acknowledging the intricate interplay between genetics and environment:
Gene-Environment Correlation
Gene-environment correlation suggests that genetic factors can influence an individual’s exposure to particular environmental conditions. For example,a genetically predisposed musical talent may lead an individual to seek out music lessons or opportunities for artistic expression.
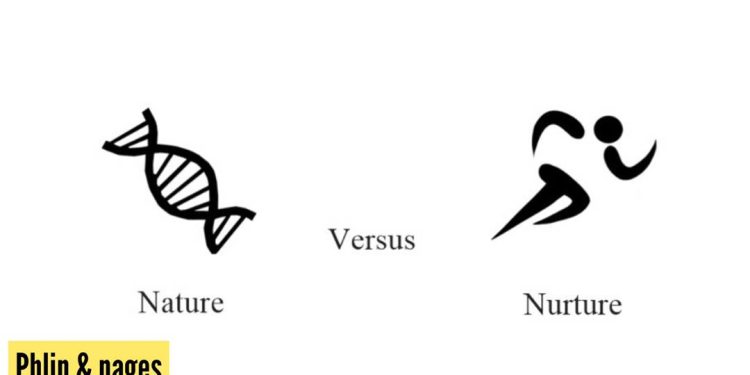
Epigenetics
Epigenetic mechanisms refer to changes in gene expression that occur without altering the underlying DNA sequence itself.These modifications can be influenced by environmental factors like stress levels,dietary patterns,and exposure to toxins.They have been shown to play a significant role in shaping behavior throughout life.
Conclusion
The nature versus nurture debate highlights how both genetics and environment contribute to shaping human behavior. While genes provide a foundation for potential traits or tendencies, it is the complex interaction between genetic predispositions and environmental experiences that ultimately shapes who we are. The interplay between nature and nurture is essential for understanding various aspects of human development and behavior. Recognizing this interdependence allows us to appreciate the diversity of human experiences while cultivating a more comprehensive understanding of the factors that influence our actions.