Psychological theories aim to explain the complex relationship between personality and behavior. These theories provide frameworks for understanding how individuals develop their unique personalities, as well as how these personalities influence their thoughts, emotions, and actions. This article explores some prominent psychological theories that shed light on the interplay between personality and behavior.
Psychodynamic Theory

Sigmund Freud’s psychodynamic theory suggests that human behavior is driven by unconscious motives and conflicts. According to this theory, personality consists of three components: id (primitive instincts), ego (rational self), and superego (internalized morals). Freud believed that unresolved conflicts during childhood could lead to defense mechanisms, such as repression or projection, which shape individual behaviors.
Trait Theory
Trait theory emphasizes identifying stable patterns of behavior across different situations. It suggests that each person possesses a unique combination of traits, which are enduring characteristics influencing their thoughts, feelings, and actions. Traits can be classified into various dimensions like extraversion vs introversion or openness vs closed-mindedness. Trait theorists focus on measuring these traits through assessment tools like questionnaires.
Social Learning Theory
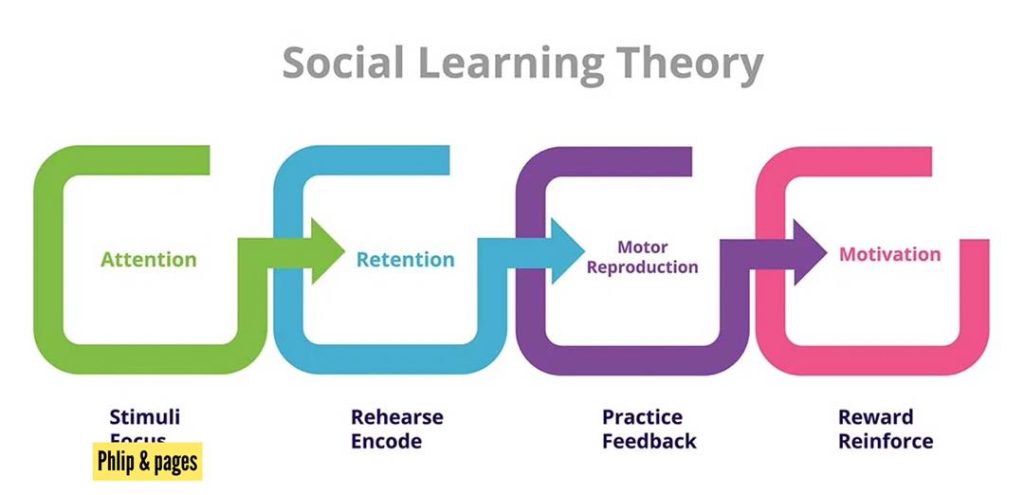
Social learning theory proposes that people learn behaviors through observation and imitation of others within social contexts. Albert Bandura’s work highlights the importance of observational learning in shaping behavior patterns. According to this theory, individuals acquire new behaviors by observing others’ actions and consequences they face for those actions. This process is influenced by cognitive factors such as attention, retention, reproduction,and motivation.
Humanistic Theory

Humanistic theories emphasize personal growth,self-actualization,and individual agency.They view humans as inherently good with an innate drive towards fulfilling their potential.Carl Rogers’ person-centered approach focuses on self-concept,the subjective perception one has about oneself.Rogers emphasized unconditional positive regard from significant others,facilitating healthy development,self-esteem,and congruence between self-perception and behavior.
Cognitive Theory

Cognitive theories explore how thoughts, beliefs,and mental processes influence personality and behavior. According to cognitive theorists like Albert Ellis or Aaron Beck, individuals’ interpretations of events shape their emotional responses and subsequent behaviors. These theories emphasize the role of cognitive distortions,negative thinking patterns,and irrational beliefs in influencing maladaptive behaviors.
Biological Theory
Biological theories suggest that genetics, brain structure,function,hormonal influences,and neurotransmitter activity contribute to personality and behavior. For example,the Five-Factor Model (FFM) of personality proposes that five broad dimensions—Openness,Conscientiousness,Extraversion,Agreeableness,and Neuroticism—are influenced by a combination of genetic predispositions and environmental factors.
Conclusion
Psychological theories offer valuable insights into understanding the complex relationship between personality and behavior. Psychodynamic theory emphasizes unconscious motives,Trait theory focuses on enduring characteristics,Social learning theory highlights observational learning processes.Humanistic approaches stress self-actualization,Cognitive theories examine thought patterns influencing behavior,Biological perspectives consider genetic,biochemical,& neurological influences.These diverse frameworks provide a comprehensive understanding of human nature,enabling researchers,counselors,and individuals themselves to gain insight,intervene effectively,promote personal growth&facilitate positive change