Emotions play a vital role in shaping human behavior. Our emotional experiences influence how we perceive, interpret, and respond to the world around us. Understanding the intricate connection between emotions and behavior is key to comprehending human actions. This article explores this relationship and delves into various ways in which emotions impact our behavior.
Emotion as a Motivator

Emotions serve as powerful motivators for human behavior. They can drive individuals towards specific actions or steer them away from others based on their subjective experiences. Here are some key aspects related to emotion as a motivator:
Approach Motivation
Positive emotions like joy, excitement, or desire often motivate individuals to approach desirable situations or pursue certain goals. These emotions generate enthusiasm and energy that propel individuals forward.
Avoidance Motivation
Negative emotions such as fear, disgust, or sadness can motivate individuals to avoid threatening stimuli or undesirable outcomes.These emotions create a sense of urgency that prompts avoidance behaviors.
Emotional Appraisal: Evaluating Situations

Emotional appraisal refers to how we evaluate situations based on our emotional responses. This evaluation influences subsequent behavioral choices. Here are two primary factors related to emotional appraisal:
Valence
Valence refers to whether an emotion is positive (e.g., happiness) or negative (e.g., anger). The valence of an emotion shapes our behavioral responses accordingly.For example,a positive emotion may lead someone to seek social interaction while a negative emotion may cause withdrawal.
Intensity
The intensity of an emotion determines its impact on behavior.Highly intense emotions tend to elicit stronger and more immediate reactions compared to milder ones.In times of extreme anger or fear,the associated behaviors might be more impulsive or extreme as well.
Influence of Emotional Regulation
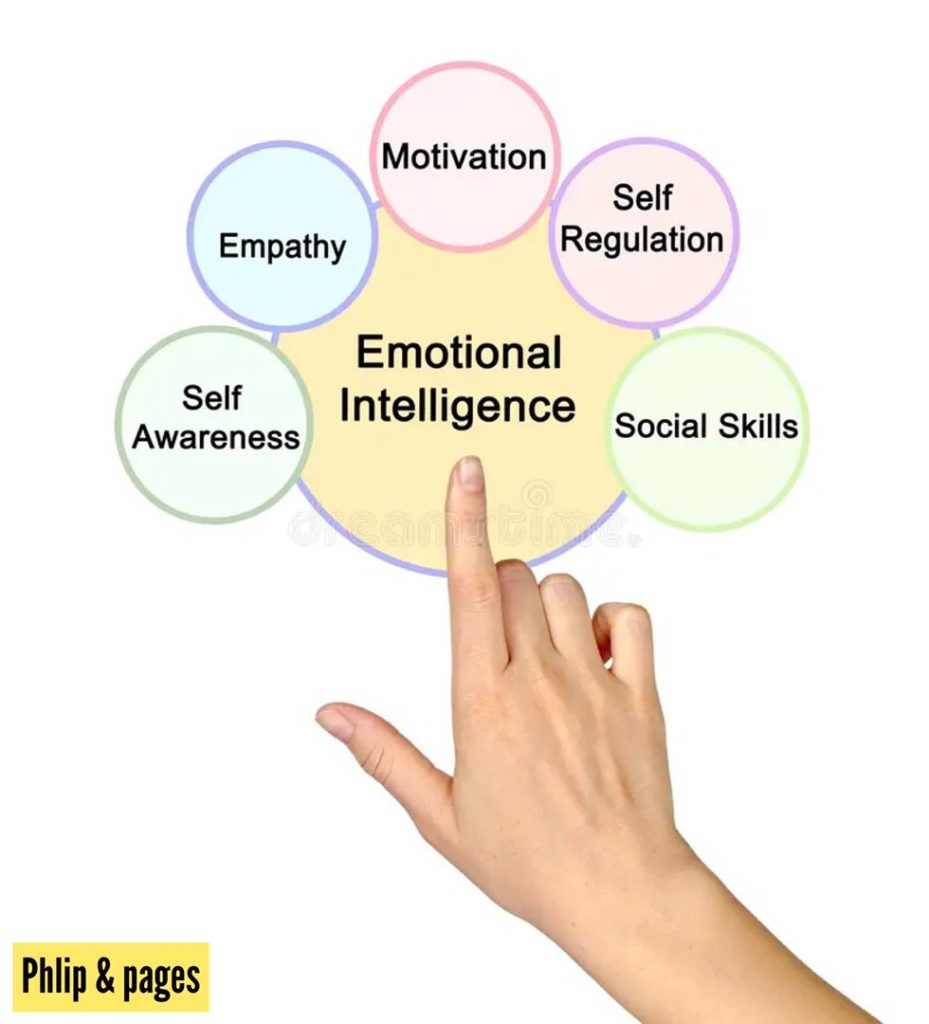
Emotional regulation involves managing one’s own feelings in order to adaptively respond to situations. Effective emotional regulation can influence behavior in various ways:
Impulse Control
Regulating emotions allows individuals to exercise impulse control, resisting impulsive or rash actions that may have negative consequences. This self-control helps individuals make more rational and adaptive choices.
Social Interactions
Emotional regulation also plays a role in social interactions. Managing emotions appropriately enables individuals to navigate social situations effectively, express empathy, and establish positive relationships.
Emotional Contagion: Spreading Emotions
Emotional contagion refers to the phenomenon where people “catch” the emotions of others. This contagiousness influences behavior as well. Here are some key points related to emotional contagion:
Mimicry
When witnessing someone else’s emotion, people often unconsciously mimic facial expressions, body language, and vocal cues associated with that emotion. This mimicry can lead to shared emotional experiences and potentially similar behavioral responses.
Empathy
Empathy is an essential component of emotional contagion. It involves understanding and sharing another person’s feelings. When we empathize with others’ emotions, it can impact our own behaviors towards them, such as offering support or assistance.
Conclusion

The connection between emotions and behavior is intricate and multidimensional. Emotions serve as motivators, influencing whether we approach or avoid certain situations. Our evaluation of emotionally-charged events shapes our subsequent behavioral choices. The ability to regulate our emotions impacts how we respond adaptively. Even the contagious nature of emotions plays a role in shaping human behavior. Recognizing these connections enhances our understanding of why people behave the way they do. By considering both individual emotional experiences and the influence of others’ emotions on use gain insight into the complex interplay between our internal states and our outward actions