Habits are deeply ingrained patterns of behavior that we engage in automatically, often without conscious thought. While habits can be beneficial, they can also contribute to negative behaviors or hinder personal growth. Understanding how habits form and learning strategies to break unhealthy cycles is essential for fostering positive change. This article explores the relationship between habits and behavior, and provides insights into breaking the cycle of unwanted habits.
Habit Formation
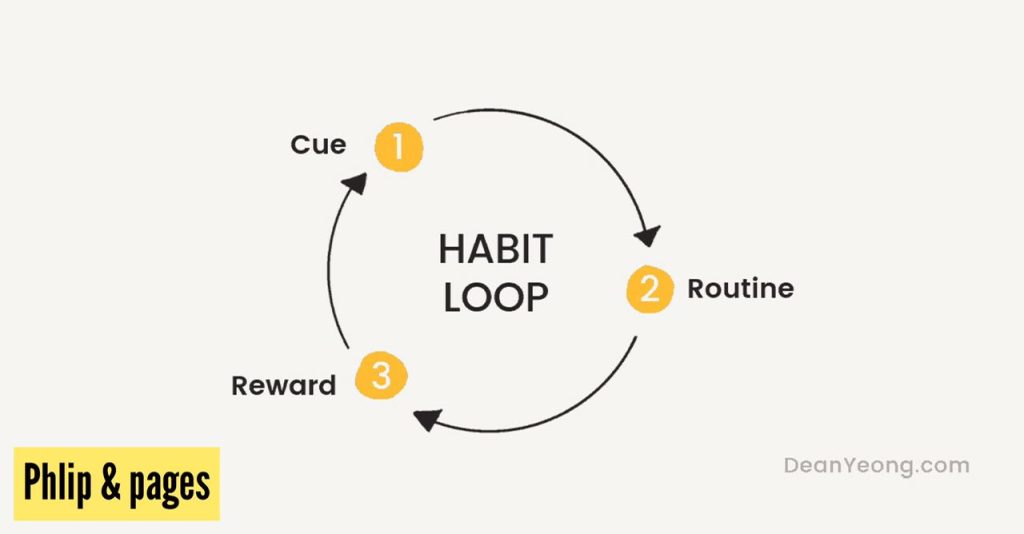
Habit formation involves a three-step loop: cue, routine, and reward. The cue triggers a specific behavior or routine, which is followed by a reward that reinforces the habit loop. Over time, this repetition solidifies the habit as it becomes increasingly automatic.
Identifying Cues
To break an unwanted habit, it’s crucial to identify the cues that trigger it. Cues can be internal (such as emotions or physical sensations) or external (such as time of day or environmental triggers). By recognizing these cues, we gain awareness of when our undesirable behaviors tend to occur.
Analyzing Rewards
Understanding what rewards we derive from our habits is equally important. Rewards satisfy certain cravings or desires—whether emotional (e.g., stress relief) or physical (e.g., pleasure). Analyzing these rewards helps uncover underlying motivations behind our behaviors.
Strategies for Breaking Unwanted Habits

Breaking unwanted habits requires intentional effort and commitment.Here are some effective strategies:
Replace with Alternatives
Identify healthier alternatives that fulfill similar needs.Consciously substitute unhealthy routines with more positive ones.For example,replacing late-night snacking with reading before bed can help redirect your behavior while still satisfying relaxation needs.
Modify Environmental Triggers
Alter your environment to minimize exposure to cues associated with undesired behaviors.This might involve rearranging your workspace,to avoid distractions during work hours.Or,you could remove tempting snacks from your pantry if you’re trying to reduce mindless eating.
Practice Mindfulness
Cultivating mindfulness can increase awareness of your thoughts,emotions,and bodily sensations.Incorporate mindfulness techniques like meditation or deep breathing to pause and observe your impulses.This self-awareness empowers you to make conscious choices instead of acting on autopilot.
Seek Support
Engaging in social support networks can provide encouragement and accountability.Share your goals with trusted friends,family members,or support groups.They can offer guidance,sympathy,and motivation during challenging times.
Persistence and Self-Compassion

Breaking unwanted habits is a process that requires persistence and self-compassion. Here are some key points to remember:
Patience
Changing deeply ingrained habits takes time.Be patient with yourself as setbacks may occur.Remind yourself that progress is not always linear,but each effort contributes to long-term change.
Learn from Setbacks
View setbacks as learning opportunities rather than failures.Reflect on the triggers or situations that led to the undesired behavior.Adjust your strategies accordingly,to better equip yourself for future challenges.
Practice Self-Compassion
Be kind and compassionate towards yourself throughout this journey.Acknowledge that breaking habits can be challenging.Treat yourself with understanding,resilience,and forgiveness when faced with obstacles or relapses.
Conclusion

Habits significantly influence our behavior patterns.Understanding how habits form through cues,routines, and rewards allows us to analyze their underlying mechanisms.Breaking unwanted habits involves identifying cues,replacing routines,modifying environments,cultivating mindfulness,and seeking support.Practice patience,self-reflection,persistence,and self-compassion throughout this process.Remember,you have the power to reshape behaviors by deliberately creating new patterns.Enabling positive change leads to personal growth,self-improvement,and an enhanced quality of life.