Space exploration has yielded many fascinating discoveries that have expanded our understanding of the universe and our place within it. Here are some of the most notable findings:
1. Exoplanets
- Discovery of Kepler-186f: This Earth-sized planet in the habitable zone of its star suggests that potentially life-supporting planets are more common than previously thought.
- TRAPPIST-1 System: Seven Earth-sized planets orbiting a single star, with three in the habitable zone, have raised hopes of finding extraterrestrial life.
2. Water on Mars
- Liquid Water: Evidence of liquid water on Mars, such as recurring slope lineae (RSL), suggests that the planet may have been habitable in the past and could still support microbial life.
- Ice Deposits: Large quantities of water ice have been found beneath the Martian surface, which could be crucial for future human missions.
3. Black Holes
- First Image of a Black Hole: The Event Horizon Telescope captured the first-ever image of a black hole in the galaxy M87, providing visual evidence of these mysterious objects.
- Gravitational Waves: LIGO’s detection of gravitational waves confirmed a major prediction of Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity and provided new ways to observe cosmic events like black hole mergers.
4. Dark Matter and Dark Energy
- Dark Matter Evidence: Observations of galaxy rotations and gravitational lensing support the existence of dark matter, which constitutes about 27% of the universe’s mass-energy content.
- Dark Energy Discovery: The accelerating expansion of the universe, attributed to dark energy, has profound implications for the fate of the cosmos and makes up roughly 68% of the universe.
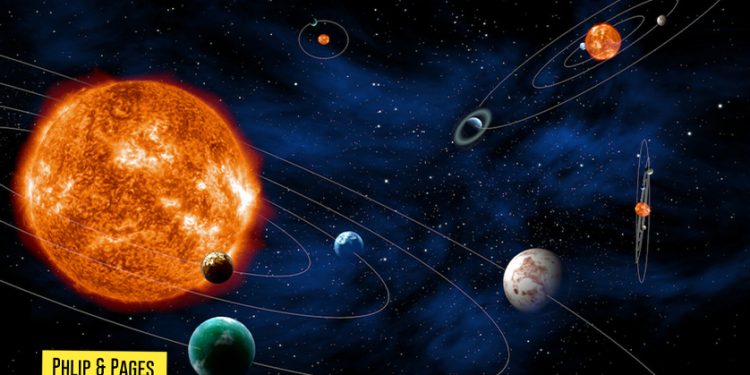
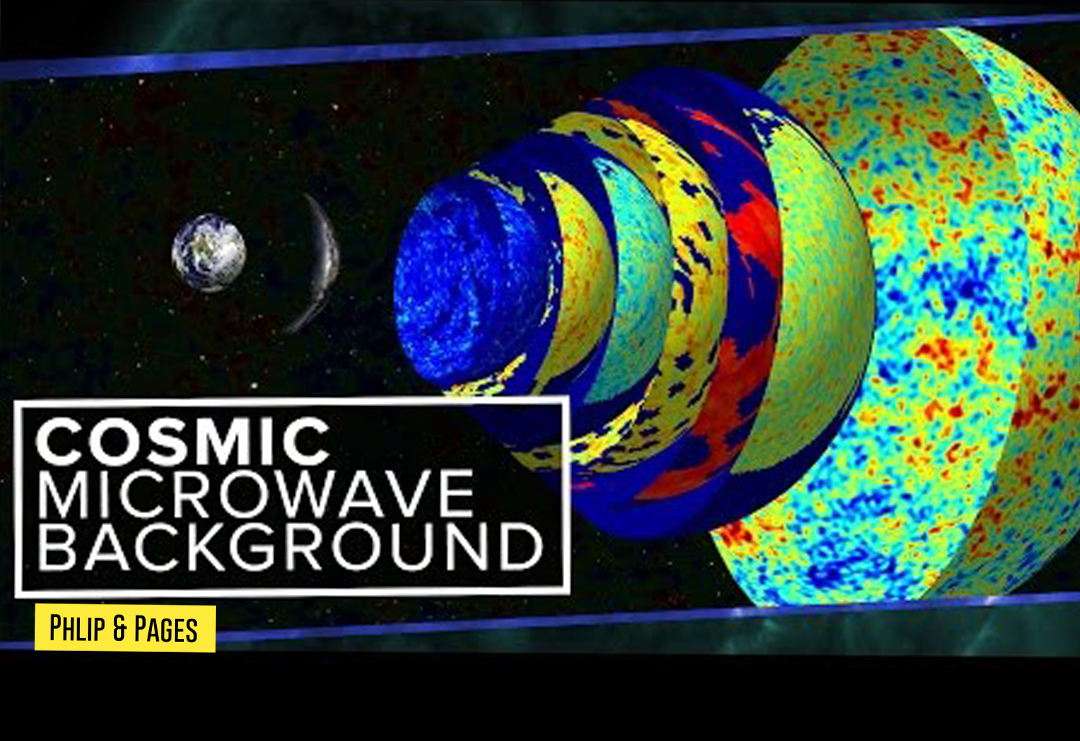
5. Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB)
- CMB Mapping: The Planck satellite provided detailed maps of the CMB, offering insights into the universe’s early conditions and supporting the Big Bang theory.
6. Voyager Missions
- Interstellar Space: Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 have entered interstellar space, providing unprecedented data about the heliosphere and the interstellar medium.
7. Saturn’s Moons
- Enceladus: The discovery of water plumes and a subsurface ocean on Enceladus suggests the potential for microbial life.
- Titan: Titan’s lakes of liquid methane and ethane, and the presence of complex organic molecules, make it a target for studying prebiotic chemistry.
8. Pluto and the Kuiper Belt
- New Horizons Mission: The New Horizons flyby revealed Pluto’s diverse geology, including ice mountains and a possible subsurface ocean, challenging our understanding of these distant objects.
9. Mars Rovers
- Curiosity: Discoveries of organic molecules and fluctuating methane levels on Mars by the Curiosity rover indicate potential signs of past or present life.
- Perseverance: The search for biosignatures and the collection of samples for future return missions aim to answer questions about life on Mars.
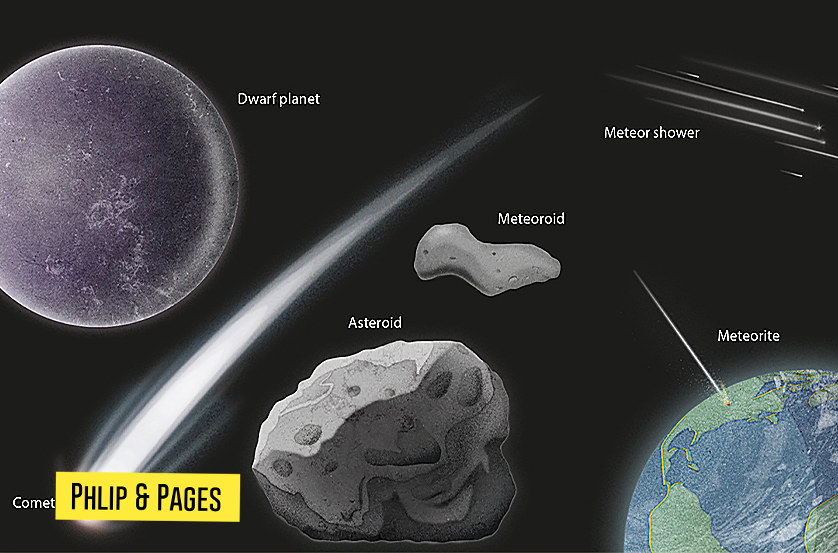
10. Asteroids and Comets
- Rosetta and Philae: The Rosetta mission’s landing on Comet 67P provided valuable data on comet composition and activity.
- OSIRIS-REx and Hayabusa2: These missions successfully collected samples from asteroids Bennu and Ryugu, respectively, offering insights into the early solar system.
11. Extragalactic Discoveries
- Andromeda-Milky Way Collision: Studies predict a future collision between the Andromeda galaxy and the Milky Way, which will significantly reshape our galaxy.
- High-Redshift Galaxies: Observations of distant galaxies formed shortly after the Big Bang help us understand the early universe’s structure and evolution.
12. Mysterious Phenomena
- Fast Radio Bursts (FRBs): These brief, intense bursts of radio waves from distant galaxies are still not fully understood, sparking numerous theories about their origins.
- Tabby’s Star: Unusual dimming patterns in this star have led to various hypotheses, including the possibility of an alien megastructure.
Conclusion
These discoveries highlight the incredible progress in space exploration and the continuous expansion of our knowledge about the universe. Each finding not only answers existing questions but also raises new ones, fueling the ongoing quest to understand the cosmos.